主要信息
Target
Tyrosine Hydroxylase
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat,
Applications
WB, IF, ELISA
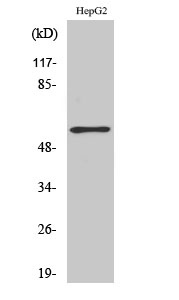
MW
58kD (Calculated)
59kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
货号: YM33070
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
现货
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
现货
0
40μL
¥960.00
现货
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
详细信息
推荐稀释比
WB 1:500-2000; IF 1:100-500; ELISA 1:1000-5000
组成
PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300, 0.05%BSA
特异性
This antibody detects endogenous levels of Tyrosine Hydroxylase protein.
纯化工艺
Protein G
储存
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
浓度
1 mg/ml
理论分子量
58kD
实测条带
59kD
修饰
Unmodified
克隆性
Monoclonal
克隆号
PTR2544
同种型
IgG1,Kappa
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
免疫原:
Synthesized peptide derived from human Tyrosine Hydrolase AA range: 1-100
展开内容
特异性:
This antibody detects endogenous levels of Tyrosine Hydroxylase protein.
展开内容
基因名称:
TH TYH
展开内容
蛋白名称:
Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase (Tyrosine 3-hydroxylase) (TH),Tyrosine Hydrolase
展开内容
别名:
Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase ;
Tyrosine 3-hydroxylase ;
TH ;
Tyrosine 3-hydroxylase ;
TH ;
展开内容
背景:
The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine. It is the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of catecholamines, hence plays a key role in the physiology of adrenergic neurons. Mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal recessive Segawa syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been noted for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
展开内容
功能:
Catalytic activity:L-tyrosine + tetrahydrobiopterin + O(2) = 3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine + 4a-hydroxytetrahydrobiopterin.,cofactor:Fe(2+) ion.,Disease:Defects in TH are the cause of dystonia DOPA-responsive autosomal recessive (ARDRD) [MIM:605407]; also known as autosomal recessive Segawa syndrome. ARDRD is a form of DOPA-responsive dystonia presenting in infancy or early childhood. Dystonia is defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contractions, often leading to abnormal postures. Some cases of ARDRD present with parkinsonian symptoms in infancy. Unlike all other forms of dystonia, it is an eminently treatable condition, due to a favorable response to L-DOPA.,enzyme regulation:Phosphorylation leads to an increase in the catalytic activity.,Function:Plays an important role in the physiology of adrenergic neurons.,online information:Tyrosine hydroxylase entry,pathway:Catecholamine biosynthesis; dopamine biosynthesis; dopamine from L-tyrosine: step 1/2.,similarity:Belongs to the biopterin-dependent aromatic amino acid hydroxylase family.,tissue specificity:Mainly expressed in the brain and adrenal glands.,
展开内容
组织表达:
Mainly expressed in the brain and adrenal glands.
展开内容
研究领域:
>>Tyrosine metabolism ;
>>Folate biosynthesis ;
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Dopaminergic synapse ;
>>Prolactin signaling pathway ;
>>Parkinson disease ;
>>Cocaine addiction ;
>>Amphetamine addiction ;
>>Alcoholism
>>Folate biosynthesis ;
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Dopaminergic synapse ;
>>Prolactin signaling pathway ;
>>Parkinson disease ;
>>Cocaine addiction ;
>>Amphetamine addiction ;
>>Alcoholism
展开内容
信号通路
文献引用({{totalcount}})
货号: YM33070
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
现货
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
现货
0
40μL
¥960.00
现货
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}









.jpg)