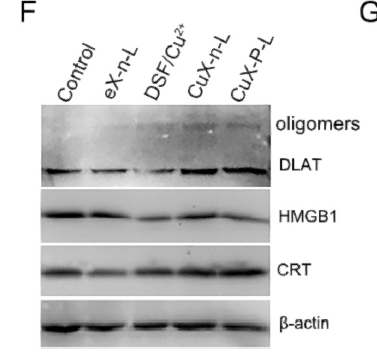
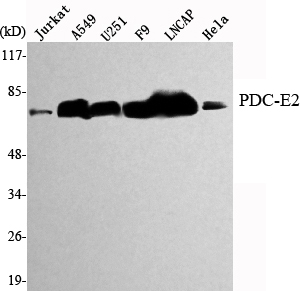
主要信息
Target
PDC-E2
Host Species
Mouse
Reactivity
Human, Mouse
Applications
WB, ICC, IP
MW
69kD (Observed)
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified
货号: YM1328
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
一周
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
一周
0
40μL
¥960.00
一周
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
详细信息
推荐稀释比
WB 1:1000; ICC 1:300
组成
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
特异性
This antibody detects endogenous levels of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase E2 and does not cross-react with related proteins.
纯化工艺
The antibody was affinity-purified from mouse ascites by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
储存
-15°C to -25°C/1 year(Do not lower than -25°C)
实测条带
69kD
修饰
Unmodified
克隆性
Monoclonal
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
免疫原:
Purified recombinant human Pyruvate Dehydrogenase E2 protein fragments expressed in E.coli.
展开内容
特异性:
This antibody detects endogenous levels of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase E2 and does not cross-react with related proteins.
展开内容
基因名称:
DLAT
展开内容
别名:
70 kDa mitochondrial autoantigen of primary biliary cirrhosis ;
anti DLAT ;
Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex ;
Dihydrolipoamide ;
Dihydrolipoamide S Acetyltransferase ;
Dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase ;
E2 component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex ;
Dihydrolipoamide S-Acetyltransferase ;
Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex ;
dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex mitochondrial ;
DLAT ;
DLAT ;
DLTA ;
E2 ;
E2 component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex ;
M2 antigen complex 70 kDa subunit ;
M2 Antigen Complex 70kD Subunit ;
mitochondrial ;
ODP2_HUMAN ;
PBC ;
PDC E2 ;
PDC-E2 ;
PDCE2 ;
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex component E2 ;
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E2 subunit ;
S acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
anti DLAT ;
Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex ;
Dihydrolipoamide ;
Dihydrolipoamide S Acetyltransferase ;
Dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase ;
E2 component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex ;
Dihydrolipoamide S-Acetyltransferase ;
Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex ;
dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex mitochondrial ;
DLAT ;
DLAT ;
DLTA ;
E2 ;
E2 component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex ;
M2 antigen complex 70 kDa subunit ;
M2 Antigen Complex 70kD Subunit ;
mitochondrial ;
ODP2_HUMAN ;
PBC ;
PDC E2 ;
PDC-E2 ;
PDCE2 ;
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex component E2 ;
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E2 subunit ;
S acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
展开内容
背景:
This gene encodes component E2 of the multi-enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC). PDC resides in the inner mitochondrial membrane and catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A. The protein product of this gene, dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase, accepts acetyl groups formed by the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate and transfers them to coenzyme A. Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase is the antigen for antimitochondrial antibodies. These autoantibodies are present in nearly 95% of patients with the autoimmune liver disease primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). In PBC, activated T lymphocytes attack and destroy epithelial cells in the bile duct where this protein is abnormally distributed and overexpressed. PBC enventually leads to cirrhosis and liver failure. Mutations in this gene are also a cause of pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 deficiency which causes primary lact
展开内容
功能:
Catalytic activity:Acetyl-CoA + enzyme N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine = CoA + enzyme N(6)-(S-acetyldihydrolipoyl)lysine.,cofactor:Binds 2 lipoyl cofactors covalently.,Disease:Defects in DLAT are the cause of pyruvate dehydrogenase E2 deficiency [MIM:245348]; also known as lactic acidemia due to defect of E2 lipoyl transacetylase of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) deficiency is a major cause of primary lactic acidosis and neurological dysfunction in infancy and early childhood. In this form of PDH deficiency episodic dystonia is the major neurological manifestation, with other more common features of pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency, such as hypotonia and ataxia, being less prominent.,Disease:Primary biliary cirrhosis is a chronic, progressive cholestatic liver disease characterized by the presence of antimitochondrial autoantibodies in patients' serum. It manifests with inflammatory obliteration of intra-hepatic bile duct, leading to liver cell damage and cirrhosis. Patients with primary biliary cirrhosis show autoantibodies against the E2 component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.,Function:The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2). It contains multiple copies of three enzymatic components: pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1), dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase (E2) and lipoamide dehydrogenase (E3).,sequence Caution:Contaminating sequence. Sequence of unknown origin in the N-terminal part.,similarity:Belongs to the 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase family.,similarity:Contains 1 lipoyl-binding domain.,similarity:Contains 2 lipoyl-binding domains.,subunit:20 to 30 alpha(2)-beta(2) tetramers of E1 + 6 homodimers of E3 + 60 copies of E2.,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Mitochondrion matrix.
展开内容
组织表达:
Heart,Keratinocyte carcinoma,Kidney,Liver,Placenta,Testis,
展开内容
研究领域:
>>Glycolysis / Gluconeogenesis ;
>>Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) ;
>>Pyruvate metabolism ;
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Carbon metabolism
>>Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) ;
>>Pyruvate metabolism ;
>>Metabolic pathways ;
>>Carbon metabolism
展开内容
文献引用({{totalcount}})
货号: YM1328
规格
价格
货期
数量
200μL
¥3,780.00
一周
0
100μL
¥2,300.00
一周
0
40μL
¥960.00
一周
0
加入购物车


已收藏


收藏
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}