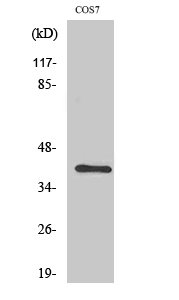
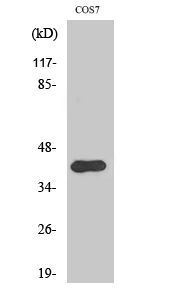
主要信息
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified

详细信息
储存
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
修饰
Unmodified
检测方法
Colorimetric
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
基因名称:
CRK
展开内容
别名:
Adapter molecule crk ;
Proto-oncogene c-Crk ;
p38 ;
Proto-oncogene c-Crk ;
p38 ;
展开内容
背景:
This gene encodes a member of an adapter protein family that binds to several tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. The product of this gene has several SH2 and SH3 domains (src-homology domains) and is involved in several signaling pathways, recruiting cytoplasmic proteins in the vicinity of tyrosine kinase through SH2-phosphotyrosine interaction. The N-terminal SH2 domain of this protein functions as a positive regulator of transformation whereas the C-terminal SH3 domain functions as a negative regulator of transformation. Two alternative transcripts encoding different isoforms with distinct biological activity have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],
展开内容
功能:
Domain:The C-terminal SH3 domain function as a negative modulator for transformation and the N-terminal SH3 domain appears to function as a positive regulator for transformation.,Domain:The SH2 domain mediates interaction with SHB.,Function:The Crk-I and Crk-II forms differ in their biological activities. Crk-II has less transforming activity than Crk-I. Crk-II mediates attachment-induced MAPK8 activation, membrane ruffling and cell motility in a Rac-dependent manner. Involved in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells and cell motility via its interaction with DOCK1 and DOCK4.,PTM:Phosphorylated on Tyr-221 upon cell adhesion. Results in the negative regulation of the association with SH2- and SH3-binding partners, possibly by the formation of an intramolecular interaction of phosphorylated Tyr-221 with the SH2 domain. This leads finally to the down-regulation of the Crk signaling pathway.,PTM:Phosphorylation of Crk-II (40 kDa) gives rise to a 42 kDa form.,similarity:Contains 1 SH2 domain.,similarity:Contains 1 SH3 domain.,similarity:Contains 2 SH3 domains.,subcellular location:Translocated to the plasma membrane upon cell adhesion.,subunit:Interacts with ABL1, C3G, SOS, MAP4K1, MAPK8 and DOCK3 via its first SH3 domain. Interacts with BCAR1, CBL, CBLB, PXN, IRS4 and GAB1 via its SH2 domain upon stimulus-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Interacts with several tyrosine-phosphorylated growth factor receptors such as EGFR, PDGFR and INSR via its SH2 domain (By similarity). Interacts with DOCK1 and DOCK4. Interacts with SHB.,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Cytoplasm . Cell membrane . Translocated to the plasma membrane upon cell adhesion. .
展开内容
信号通路
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Focal adhesion
Cellular Processes >> Cell motility >> Regulation of actin cytoskeleton
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Chemokine signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Insulin signaling pathway
Organismal Systems >> Endocrine system >> Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action
Organismal Systems >> Nervous system >> Neurotrophin signaling pathway
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> MicroRNAs in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Chronic myeloid leukemia
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Renal cell carcinoma
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> MAPK signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> ErbB signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Rap1 signaling pathway
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}