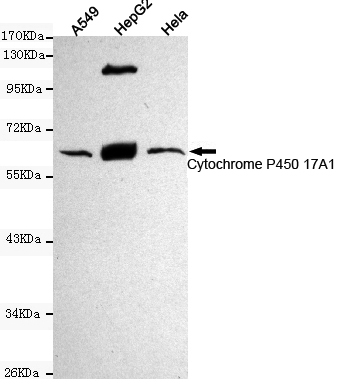
主要信息
Reactivity
Human
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified

详细信息
储存
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
修饰
Unmodified
检测方法
Colorimetric
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
基因名称:
CYP17A1
展开内容
别名:
Steroid 17-alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase ;
CYPXVII ;
Cytochrome P450 17A1 ;
Cytochrome P450-C17 ;
Cytochrome P450c17 ;
Steroid 17-alpha-monooxygenase ;
CYPXVII ;
Cytochrome P450 17A1 ;
Cytochrome P450-C17 ;
Cytochrome P450c17 ;
Steroid 17-alpha-monooxygenase ;
展开内容
背景:
catalytic activity:A steroid + AH(2) + O(2) = a 17-alpha-hydroxysteroid + A + H(2)O.,cofactor:Heme group.,disease:Defects in CYP17A1 are the cause of adrenal hyperplasia type 5 (AH5) [MIM:202110]. AH5 is a form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, a common recessive disease due to defective synthesis of cortisol. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is characterized by androgen excess leading to ambiguous genitalia in affected females, rapid somatic growth during childhood in both sexes with premature closure of the epiphyses and short adult stature. Four clinical types: "salt wasting" (SW, the most severe type), "simple virilizing" (SV, less severely affected patients), with normal aldosterone biosynthesis, "non-classic form" or late onset (NC or LOAH), and "cryptic" (asymptomatic).,enzyme regulation:Regulated predominantly by intracellular cAMP levels.,function:Conversion of pregnenolone and progesterone to their 17-alpha-hydroxylated products and subsequently to dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and androstenedione. Catalyzes both the 17-alpha-hydroxylation and the 17,20-lyase reaction. Involved in sexual development during fetal life and at puberty.,online information:The Singapore human mutation and polymorphism database,pathway:Lipid metabolism; steroid biosynthesis.,PTM:Phosphorylation is necessary for 17,20-lyase, but not for 17-alpha-hydroxylase activity.,similarity:Belongs to the cytochrome P450 family.,
展开内容
功能:
reproductive developmental process, steroid biosynthetic process, glucocorticoid biosynthetic process, sex differentiation, steroid metabolic process, glucocorticoid metabolic process, lipid biosynthetic process, response to toxin, regulation of hormone levels, cellular hormone metabolic process, hormone metabolic process, hormone biosynthetic process, oxidation reduction,
展开内容
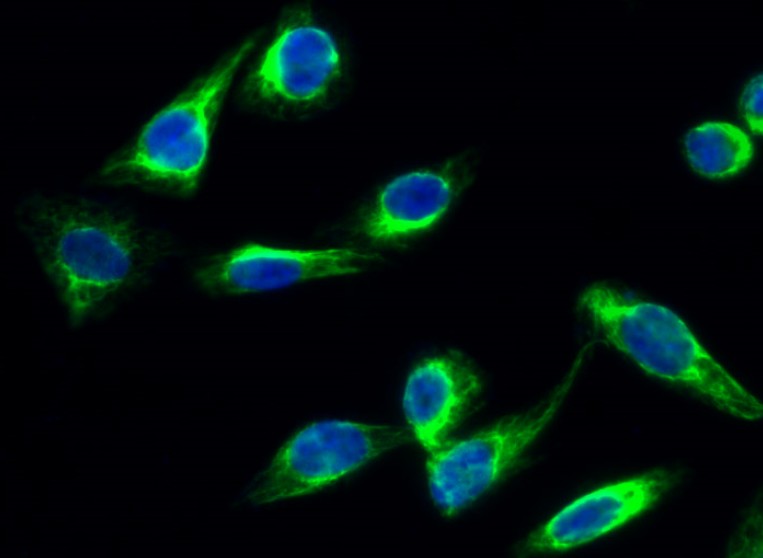
细胞定位:
Endoplasmic reticulum membrane . Microsome membrane .
展开内容
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}