主要信息
Reactivity
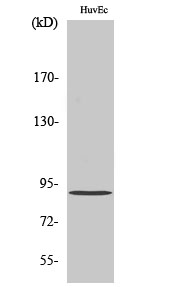
Human
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified

详细信息
储存
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
修饰
Unmodified
检测方法
Colorimetric
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
基因名称:
AKAP1
展开内容
别名:
A-kinase anchor protein 1, mitochondrial ;
A-kinase anchor protein 149 kDa ;
AKAP 149 ;
Dual specificity A-kinase-anchoring protein 1 ;
D-AKAP-1 ;
Protein kinase A-anchoring protein 1 ;
PRKA1 ;
Spermatid A-kinase anchor protein 84 ;
S-AKAP84 ;
A-kinase anchor protein 149 kDa ;
AKAP 149 ;
Dual specificity A-kinase-anchoring protein 1 ;
D-AKAP-1 ;
Protein kinase A-anchoring protein 1 ;
PRKA1 ;
Spermatid A-kinase anchor protein 84 ;
S-AKAP84 ;
展开内容
背景:
domain:RII-alpha binding site, predicted to form an amphipathic helix, could participate in protein-protein interactions with a complementary surface on the R-subunit dimer.,function:Binds to type I and II regulatory subunits of protein kinase A and anchors them to the cytoplasmic face of the mitochondrial outer membrane.,similarity:Contains 1 KH domain.,similarity:Contains 1 Tudor domain.,tissue specificity:AKAP149 is highly expressed in prostate and small intestine whereas S-AKAP84 is expressed in kidney, pancreas, liver, lung and brain. AKAP149 is also expressed in colon carcinoma.,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Mitochondrion outer membrane . Mitochondrion .
展开内容
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}