主要信息
Reactivity
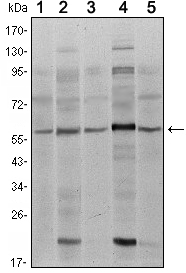
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified

详细信息
储存
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
修饰
Unmodified
检测方法
Colorimetric
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
基因名称:
SMAD4
展开内容
别名:
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 ;
MAD homolog 4 ;
Mothers against DPP homolog 4 ;
Deletion target in pancreatic carcinoma 4 ;
SMAD family member 4 ;
SMAD 4 ;
Smad4 ;
hSMAD4 ;
MAD homolog 4 ;
Mothers against DPP homolog 4 ;
Deletion target in pancreatic carcinoma 4 ;
SMAD family member 4 ;
SMAD 4 ;
Smad4 ;
hSMAD4 ;
展开内容
背景:
disease:Defects in SMAD4 are a cause of juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) [MIM:174900]; also known as juvenile intestinal polyposis (JIP). JPS is an autosomal dominant gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis syndrome in which patients are at risk for developing gastrointestinal cancers. The lesions are typified by a smooth histological appearance, predominant stroma, cystic spaces and lack of a smooth muscle core. Multiple juvenile polyps usually occur in a number of Mendelian disorders. Sometimes, these polyps occur without associated features as in JPS; here, polyps tend to occur in the large bowel and are associated with an increased risk of colon and other gastrointestinal cancers.,disease:Defects in SMAD4 are a cause of juvenile polyposis/hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia syndrome (JP/HHT) [MIM:175050]. JP/HHT syndrome phenotype consists of the coexistence of juvenile polyposis (JIP) and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) [MIM:187300] in a single individual. JIP and HHT are autosomal dominant disorders with distinct and non-overlapping clinical features. The former, an inherited gastrointestinal malignancy predisposition, is caused by mutations in SMAD4 or BMPR1A, and the latter is a vascular malformation disorder caused by mutations in ENG or ACVRL1. All four genes encode proteins involved in the transforming-growth-factor-signaling pathway. Although there are reports of patients and families with phenotypes of both disorders combined, the genetic aetiology of this association is unknown.,disease:Defects in SMAD4 are a cause of pancreatic carcinoma [MIM:260350].,disease:Defects in SMAD4 may be a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC) [MIM:114500].,function:Common mediator of signal transduction by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) superfamily; SMAD4 is the common SMAD (co-SMAD). Promotes binding of the SMAD2/SMAD4/FAST-1 complex to DNA and provides an activation function required for SMAD1 or SMAD2 to stimulate transcription. May act as a tumor suppressor.,PTM:Monoubiquitinated on Lys-519 by E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM33. Monoubiquitination hampers its ability to form a stable complex with activated SMAD2/3 resulting in inhibition of TGF-beta/BMP signaling cascade.,similarity:Belongs to the dwarfin/SMAD family.,similarity:Contains 1 MH1 (MAD homology 1) domain.,similarity:Contains 1 MH2 (MAD homology 2) domain.,subcellular location:Cytoplasmic in the absence of ligand. Migrates to the nucleus when complexed with R-SMAD.,subunit:May form trimers with receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD). Found in a ternary complex composed of SMAD4, STK11 and STK11IP. Interacts with ATF2, COPS5, DACH1, MSG1, SKI, STK11, STK11IP and TRIM33. Associates with ZNF423 or ZNF521 in response to BMP2 leading to activate transcription of BMP target genes. Interacts with USP9X.,
展开内容
功能:
regulation of cell growth, urogenital system development, metanephros development, ureteric bud development,branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis, response to hypoxia, gastrulation with mouth forming second,morphogenesis of a branching structure, regulation of cytokine production, kidney development, regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, positive regulation of protein amino acid phosphorylation, morphogenesis of an epithelium, regionalization, transcription, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, protein complex assembly, cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase signaling pathway,transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway, SMAD protein complex assembly, gastrulation, pattern specification process, negative regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of cell size, negative regulation of biosynthetic process, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, anterior/posterior pattern formation, positive regulation of signal transduction, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, negative regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, positive regulation of gene expression, negative regulation of gene expression, positive regulation of cell communication, regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition, positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition, positive regulation of cell development, regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, positive regulation of cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, positive regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation, negative regulation of transcription, regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, regulation of cell morphogenesis, neuron differentiation, negative regulation of cell growth, BMP signaling pathway, negative regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of protein modification process, positive regulation of protein modification process,regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, regulation of intracellular transport, positive regulation of intracellular transport, regulation of cellular component size, regulation of protein localization, regulation of transforming growth factor-beta2 production, regulation of intracellular protein transport, regulation of protein import into nucleus, translocation, positive regulation of protein import into nucleus, translocation, cellular macromolecular complex subunit organization, cellular macromolecular complex assembly, tube morphogenesis, tube development, regulation of growth, regulation of cell proliferation, regulation of protein import into nucleus, regulation of phosphorylation, positive regulation of phosphorylation, cellular protein complex assembly,macromolecular complex subunit organization, cell fate commitment, regulation of transcription, positive regulation of cell differentiation, negative regulation of cell size, negative regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, negative regulation of growth, negative regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of phosphate metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport, embryonic morphogenesis, neuron fate commitment, tissue morphogenesis, branching morphogenesis of a tube, positive regulation of transport, positive regulation of developmental process, regulation of binding, positive regulation of cellular component organization, negative regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, positive regulation of protein transport, regulation of protein transport, positive regulation of protein metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, negative regulation of RNA metabolic process, positive regulation of RNA metabolic process, palate development, regulation of cell development, regulation of cellular localization, regulation of SMAD protein nuclear translocation, positive regulation of SMAD protein nuclear translocation, regulation of pathway-restricted SMAD protein phosphorylation, SMAD protein signal transduction, epithelium development, epithelial tube morphogenesis, ureteric bud morphogenesis, macromolecular complex assembly, regulation of establishment of protein localization, protein complex biogenesis, response to oxygen levels,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Cytoplasmic in the absence of ligand. Migrates to the nucleus when complexed with R-SMAD (PubMed:15799969). PDPK1 prevents its nuclear translocation in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:17327236). .
展开内容
信号通路
Cellular Processes >> Cell growth and death >> Cell cycle
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Adherens junction
Cellular Processes >> Cellular community - eukaryotes >> Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells
Organismal Systems >> Immune system >> Th17 cell differentiation
Human Diseases >> Cancer: overview >> Pathways in cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Colorectal cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Pancreatic cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Hepatocellular carcinoma
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Gastric cancer
Human Diseases >> Cancer: specific types >> Chronic myeloid leukemia
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Wnt signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> TGF-beta signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Hippo signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> Apelin signaling pathway
Environmental Information Processing >> Signal transduction >> FoxO signaling pathway
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}