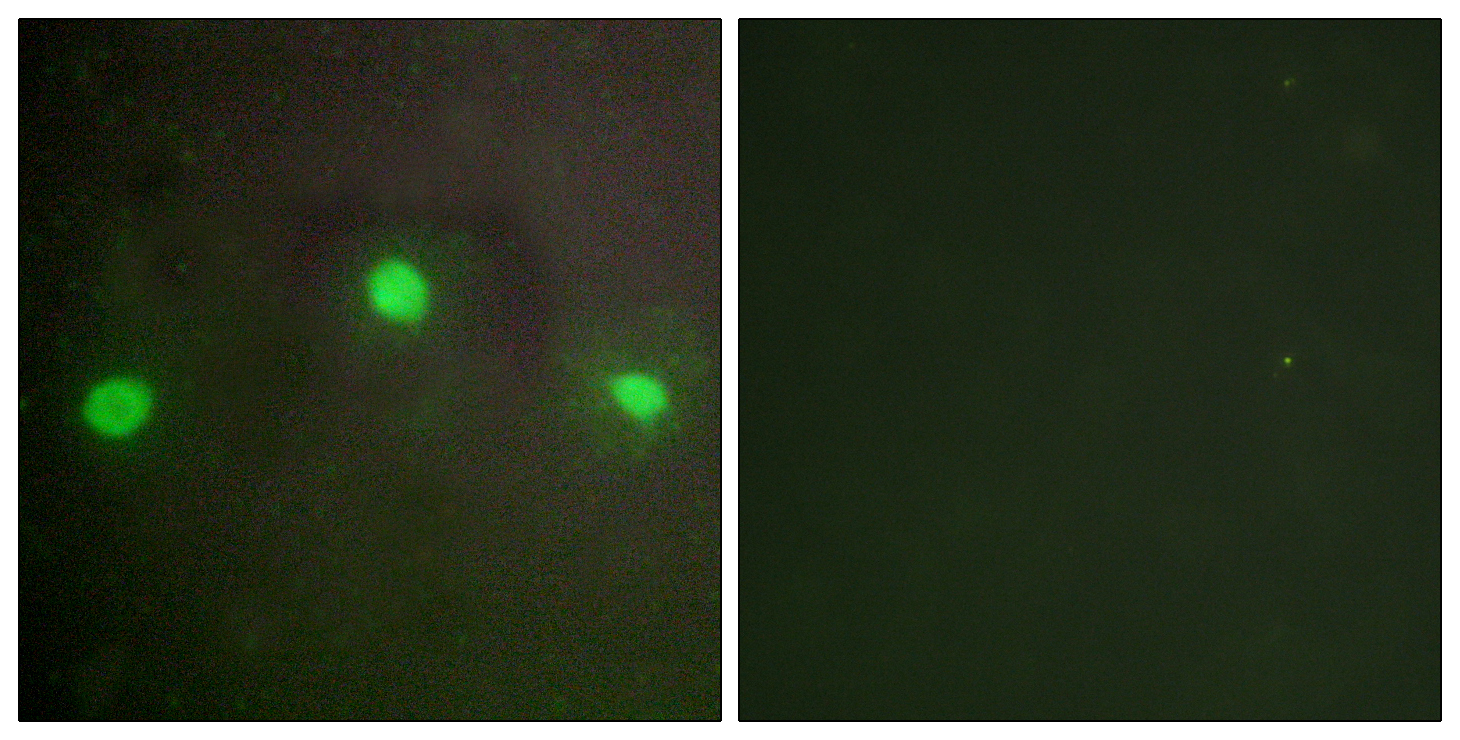
主要信息
Reactivity
Human, Mouse
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified

详细信息
储存
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
修饰
Unmodified
检测方法
Colorimetric
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
基因名称:
ATRX
展开内容
蛋白名称:
Transcriptional regulator ATRX
展开内容
别名:
ATRX ;
RAD54L ;
XH2 ;
Transcriptional regulator ATRX ;
ATP-dependent helicase ATRX ;
X-linked helicase II ;
X-linked nuclear protein ;
XNP ;
Znf-HX
RAD54L ;
XH2 ;
Transcriptional regulator ATRX ;
ATP-dependent helicase ATRX ;
X-linked helicase II ;
X-linked nuclear protein ;
XNP ;
Znf-HX
展开内容
背景:
disease:Defects in ATRX are a cause of alpha-thalassemia myelodysplasia syndrome (ATMDS) [MIM:300448]. In this disorder, alpha-thalassemia occurs as an acquired abnormality in association with a multilineage myelodysplasia.,disease:Defects in ATRX are the cause of mental retardation syndromic X-linked with hypotonic facies syndrome type 1 (MRXSHF1) [MIM:309580]; also called Carpenter-Waziri syndrome (CWS), Juberg-Marsidi syndrome (JMS), Smith-Fineman-Myers syndrome type 1 (SFM1). Clinical features include severe mental retardation, dysmorphic facies, and a highly skewed X-inactivation pattern in carrier women. Other more variable features include hypogonadism, deafness, renal anomalies, and mild skeletal defects.,disease:Defects in ATRX are the cause of X-linked alpha-thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome (ATR-X) [MIM:301040]. ATR-X is an X-linked disorder comprising severe psychomotor retardation, facial dysmorphism, urogenital abnormalities, and alpha-thalassemia. An essential phenotypic trait are hemoglobin H erythrocyte inclusions.,domain:Contains one Pro-Xaa-Val-Xaa-Leu (PxVxL) motif, which is required for interaction with chromoshadow domains. This motif requires additional residues -7, -6, +4 and +5 of the central Val which contact the chromoshadow domain.,function:Could be a global transcriptional regulator. Modifies gene expression by affecting chromatin. May be involved in brain development and facial morphogenesis.,PTM:Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR.,similarity:Belongs to the SNF2/RAD54 helicase family.,similarity:Contains 1 GATA-type zinc finger.,similarity:Contains 1 helicase ATP-binding domain.,similarity:Contains 1 helicase C-terminal domain.,similarity:Contains 1 PHD-type zinc finger.,subcellular location:Associated with pericentromeric heterochromatin during interphase and mitosis, probably by interacting with HP1.,subunit:Probably binds EZH2. Binds annexin V in a calcium and phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylserine-dependent manner (By similarity). Interacts directly with CBX5 via the PxVxL motif.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitous.,
展开内容
功能:
DNA metabolic process, DNA repair, DNA modification, DNA alkylation, DNA methylation, DNA recombination, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, one-carbon metabolic process, response to DNA damage stimulus, forebrain development, methylation, cellular response to stress, regulation of gene expression, epigenetic, biopolymer methylation, regulation of transcription, regulation of RNA metabolic process,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Nucleus. Chromosome, telomere. Nucleus, PML body. Associated with pericentromeric heterochromatin during interphase and mitosis, probably by interacting with CBX5/HP1 alpha. Colocalizes with histone H3.3, DAXX, HIRA and ASF1A at PML-nuclear bodies. Colocalizes with cohesin (SMC1 and SMC3) and MECP2 at the maternal H19 ICR (By similarity). .
展开内容
组织表达:
展开内容
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}