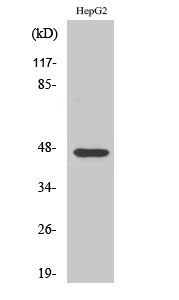
主要信息
Reactivity
Human
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Unmodified

详细信息
储存
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
修饰
Unmodified
检测方法
Colorimetric
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
基因名称:
AKAP5
展开内容
别名:
A-kinase anchor protein 5 ;
AKAP-5 ;
A-kinase anchor protein 79 kDa ;
AKAP 79 ;
H21 ;
cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit II high affinity-binding protein ;
AKAP-5 ;
A-kinase anchor protein 79 kDa ;
AKAP 79 ;
H21 ;
cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit II high affinity-binding protein ;
展开内容
背景:
domain:RII-alpha binding site, predicted to form an amphipathic helix, could participate in protein-protein interactions with a complementary surface on the R-subunit dimer.,function:May anchor the PKA protein to cytoskeletal and/or organelle-associated proteins, targeting the signal carried by cAMP to specific intracellular effectors. Association with to the beta2-adrenergic receptor (beta2-AR) not only regulates beta2-AR signaling pathway, but also the activation by PKA by switching off the beta2-AR signaling cascade.,miscellaneous:The N-terminal region, which is highly basic, is required for interaction with calmodulin.,similarity:Contains 1 AKAP domain.,subcellular location:Associated with particulate fractions.,subunit:Binding protein for dimer of the RII-beta regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and also for the protein kinase C (PKC) and the phosphatase calcineurin (PP2B). Each enzyme is inhibited when bound to the anchoring protein. Also binds the beta2-adrenergic receptor.,tissue specificity:Predominantly in the cerebral cortex and the postsynaptic densities of the forebrain, and to a lesser extent in adrenal medulla, lung and anterior pituitary.,
展开内容
功能:
protein targeting, intracellular protein transport, cell-cell signaling, synaptic transmission, protein localization, protein transport, transmission of nerve impulse, regulation of organelle organization, cellular protein localization,establishment of protein localization, intracellular transport, neurological system process, regulation of cytoskeleton organization, cellular macromolecule localization,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Postsynaptic recycling endosome membrane ; Lipid-anchor . Associates with lipid rafts. .
展开内容
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}