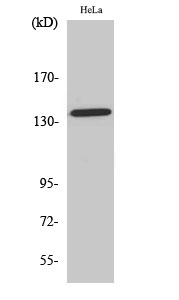
主要信息
Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat
Applications
ELISA
Conjugate/Modification
Phospho

详细信息
储存
2-8°C/6 months,Ship by ice bag
修饰
Phospho
检测方法
Colorimetric
相关产品
抗原&靶点信息
基因名称:
APP
展开内容
别名:
Amyloid beta A4 protein ;
ABPP ;
APPI ;
APP ;
Alzheimer disease amyloid protein ;
Cerebral vascular amyloid peptide ;
CVAP ;
PreA4 ;
Protease nexin-II ;
PN-II ;
[Cleaved into: N-APP ;
Soluble APP-alpha ;
S-APP-alpha ;
Soluble APP-beta ;
S-APP-beta ;
C99 ;
Beta-amyloid protein 42 ;
Beta-APP42 ;
Beta-amyloid protein 40 ;
Beta-APP40 ;
C83 ;
P3 ;
42 ;
P3 ;
40 ;
C80 ;
Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 59 ;
Amyloid intracellular domain 59 ;
AICD-59 ;
AID ;
59 ;
Gamma-CTF ;
59 ;
Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 57 ;
Amyloid intracellular domain 57 ;
AICD-57 ;
AID ;
57 ;
Gamma-CTF ;
57 ;
Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 50 ;
Amyloid intracellular domain 50 ;
AICD-50 ;
AID ;
50 ;
Gamma-CTF ;
50 ;
C31]
ABPP ;
APPI ;
APP ;
Alzheimer disease amyloid protein ;
Cerebral vascular amyloid peptide ;
CVAP ;
PreA4 ;
Protease nexin-II ;
PN-II ;
[Cleaved into: N-APP ;
Soluble APP-alpha ;
S-APP-alpha ;
Soluble APP-beta ;
S-APP-beta ;
C99 ;
Beta-amyloid protein 42 ;
Beta-APP42 ;
Beta-amyloid protein 40 ;
Beta-APP40 ;
C83 ;
P3 ;
42 ;
P3 ;
40 ;
C80 ;
Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 59 ;
Amyloid intracellular domain 59 ;
AICD-59 ;
AID ;
59 ;
Gamma-CTF ;
59 ;
Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 57 ;
Amyloid intracellular domain 57 ;
AICD-57 ;
AID ;
57 ;
Gamma-CTF ;
57 ;
Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 50 ;
Amyloid intracellular domain 50 ;
AICD-50 ;
AID ;
50 ;
Gamma-CTF ;
50 ;
C31]
展开内容
背景:
alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist. Experimental confirmation may be lacking for some isoforms,disease:Defects in APP are the cause of Alzheimer disease type 1 (AD1) [MIM:104300]. AD1 is a familial early-onset form of Alzheimer disease. It can be associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Alzheimer disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive dementia, loss of cognitve abilities, and deposition of fibrillar amyloid proteins as intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles, extracellular amyloid plaques and vascular amyloid deposits. The major constituent of these plaques is the neurotoxic amyloid-beta-APP 40-42 peptide (s), derived proteolytically from the transmembrane precursor protein APP by sequential secretase processing. The cytotoxic C-terminal fragments (CTFs) and the caspase-cleaved products such as C31 derived from APP, are also implicated in neuronal death.,disease:Defects in APP are the cause of amyloidosis cerebroarterial Dutch type (AMYLCAD) [MIM:605714]; also known as hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis Dutch type (HCHWAD). AMYLCAD is a hereditary localized amyloidosis due to amyloid-beta A4 peptide(s) deposition in the cerebral vessels. Beta-APP40 is the predominant form of cerebrovascular amyloid. Amyloid is not found outside the nervous system. The principal clinical characteristics are recurrent cerebral and cerebellar hemorrhages, recurrent strokes, cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, and progressive mental deterioration. Onset of the disease is in middle age (44 to 60 years). Patients develop cerebral hemorrhage because of the severe cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Parenchymal amyloid deposits are rare and largely in the form of pre-amyloid lesions or diffuse plaque-like structures. They are Congo red negative and lack the dense amyloid cores commonly present in Alzheimer disease.,disease:Defects in APP are the cause of amyloidosis cerebroarterial Iowa type (AMYLCAIW) [MIM:605714]. AMYLCAIW is a hereditary amyloidosis due to amyloid-beta A4 peptide(s) deposition. Patients have progressive aphasic dementia, leukoencephalopathy, and occipital calcifications.,disease:Defects in APP are the cause of amyloidosis cerebroarterial Italian type (AMYLCAIT) [MIM:605714]. AMYLCAIT is a hereditary localized amyloidosis due to amyloid-beta A4 peptide(s) deposition in the cerebral vessels, resulting in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Amyloid is not found outside the nervous system. It is a condition very similar to AMYLCAD, but the clinical course is less severe. Patients manifest mild cognitive decline, recurrent strokes, and epilepsy in some cases. There are extensive amyloid deposits in leptomeningeal and cortical vessels and, to a lesser extent, in the neuropil of the cerebral cortex, in the absence of neurofibrillary tangles.,domain:The basolateral sorting signal (BaSS) is required for sorting of membrane proteins to the basolateral surface of epithelial cells.,domain:The NPXY sequence motif found in many tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins is required for the specific binding of the PID domain. However, additional amino acids either N- or C-terminal to the NPXY motif are often required for complete interaction. The PID domain-containing proteins which bind APP require the YENPTY motif for full interaction. These interactions are independent of phosphorylation on the terminal tyrosine residue. The NPXY site is also involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis.,function:Appicans elicit adhesion of neural cells to the extracellular matrix and may regulate neurite outgrowth in the brain.,function:Beta-amyloid peptides are lipophilic metal chelators with metal-reducing activity. Bind transient metals such as copper, zinc and iron. In vitro, can reduce Cu(2+) and Fe(3+) to Cu(+) and Fe(2+), respectively. Beta-amyloid 42 is a more effective reductant than beta-amyloid 40. Beta-amyloid peptides bind to lipoproteins and apolipoproteins E and J in the CSF and to HDL particles in plasma, inhibiting metal-catalyzed oxidation of lipoproteins. Beta-APP42 may activate mononuclear phagocytes in the brain and elicit inflammatory responses. Promotes both tau aggregation and TPK II-mediated phosphorylation. Interaction with overexpressed HADH2 leads to oxidative stress and neurotoxicity.,function:Functions as a cell surface receptor and performs physiological functions on the surface of neurons relevant to neurite growth, neuronal adhesion and axonogenesis. Involved in cell mobility and transcription regulation through protein-protein interactions. Can promote transcription activation through binding to APBB1-HTATIP and inhibits Notch signaling through interaction with Numb. Couples to apoptosis-inducing pathways such as those mediated by G(O) and JIP. Inhibits G(o) alpha ATPase activity (By similarity). Acts as a kinesin I membrane receptor, mediating the axonal transport of beta-secretase and presenilin 1. Involved in copper homeostasis/oxidative stress through copper ion reduction. In vitro, copper-metallated APP induces neuronal death directly or is potentiated through Cu(2+)-mediated low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Can regulate neurite outgrowth through binding to components of the extracellular matrix such as heparin and collagen I and IV. The splice isoforms that contain the BPTI domain possess protease inhibitor activity.,function:The gamma-CTF peptides as well as the caspase-cleaved peptides, including C31, are potent enhancers of neuronal apoptosis.,induction:Increased levels during neuronal differentiation.,mass spectrometry: PubMed:12214090,miscellaneous:Chelation of metal ions, notably copper, iron and zinc, can induce histidine-bridging between beta-amyloid molecules resulting in beta-amyloid-metal aggregates. The affinity for copper is much higher than for other transient metals and is increased under acidic conditions. Extracellular zinc-binding increases binding of heparin to APP and inhibits collagen-binding.,online information:Amyloid beta entry,online information:APP mutations,PTM:Extracellular binding and reduction of copper, results in a corresponding oxidation of Cys-144 and Cys-158, and the formation of a disulfide bond. In vitro, the APP-Cu(+) complex in the presence of hydrogen peroxide results in an increased production of beta-amyloid-containing peptides.,PTM:N- and O-glycosylated. O-linkage of chondroitin sulfate to the L-APP isoforms produces the APP proteoglycan core proteins, the appicans. The chondroitin sulfate chain of appicans contains 4-O-sulfated galactose in the linkage region and chondroitin sulfate E in the repeated disaccharide region.,PTM:Phosphorylation in the C-terminal on tyrosine, threonine and serine residues is neuron-specific. Phosphorylation can affect APP processing, neuronal differentiation and interaction with other proteins. Phosphorylated on Thr-743 in neuronal cells by Cdc5 kinase and Mapk10, in dividing cells by Cdc2 kinase in a cell-cycle dependent manner with maximal levels at the G2/M phase and, in vitro, by GSK-3-beta. The Thr-743 phosphorylated form causes a conformational change which reduces binding of Fe65 family members. Phosphorylation on Tyr-757 is required for SHC binding. Phosphorylated in the extracellular domain by casein kinases on both soluble and membrane-bound APP. This phosphorylation is inhibited by heparin.,PTM:Proteolytically cleaved by caspases during neuronal apoptosis. Cleavage at Asp-739 by either caspase-6, -8 or -9 results in the production of the neurotoxic C31 peptide and the increased production of beta-amyloid peptides.,PTM:Proteolytically processed under normal cellular conditions. Cleavage by alpha-secretase or alternatively by beta-secretase leads to generation and extracellular release of soluble APP peptides, S-APP-alpha and S-APP-beta, respectively, and the retention of corresponding membrane-anchored C-terminal fragments, C83 and C99. Subsequent processing of C83 by gamma-secretase yields P3 peptides. This is the major secretory pathway and is non-amyloidogenic. Alternatively, presenilin/nicastrin-mediated gamma-secretase processing of C99 releases the amyloid beta proteins, amyloid-beta 40 (Abeta40) and amyloid-beta 42 (Abeta42), major components of amyloid plaques, and the cytotoxic C-terminal fragments, gamma-CTF(50), gamma-CTF(57) and gamma-CTF(59).,sequence caution:Contamination by an Alu repeat.,similarity:Belongs to the APP family.,similarity:Contains 1 BPTI/Kunitz inhibitor domain.,subcellular location:Cell surface protein that rapidly becomes internalized via clathrin-coated pits. During maturation, the immature APP (N-glycosylated in the endoplasmic reticulum) moves to the Golgi complex where complete maturation occurs (O-glycosylated and sulfated). After alpha-secretase cleavage, soluble APP is released into the extracellular space and the C-terminal is internalized to endosomes and lysosomes. Some APP accumulates in secretory transport vesicles leaving the late Golgi compartment and returns to the cell surface. Gamma-CTF(59) peptide is located to both the cytoplasm and nuclei of neurons. It can be translocated to the nucleus through association with APBB1 (Fe65). Beta-APP42 associates with FRPL1 at the cell surface and the complex is then rapidly internalized. APP sorts to the basolateral surface in epithelial cells. During neuronal differentiation, the Thr-743 phosphorylated form is located mainly in growth cones, moderately in neurites and sparingly in the cell body. Casein kinase phosphorylation can occur either at the cell surface or within a post-Golgi compartment.,subunit:Binds, via its C-terminus, to the PID domain of several cytoplasmic proteins, including APBB family members, the APBA family, MAPK8IP1, SHC1 and, Numb and Dab1 (By similarity). Binding to Dab1 inhibits its serine phosphorylation (By similarity). Also interacts with GPCR-like protein BPP, FPRL1, APPBP1, IB1, KNS2 (via its TPR domains) (By similarity), APPBP2 (via BaSS) and DDB1. In vitro, it binds MAPT via the MT-binding domains (By similarity). Associates with microtubules in the presence of ATP and in a kinesin-dependent manner (By similarity). Interacts, through a C-terminal domain, with GNAO1. Amyloid beta-42 binds CHRNA7 in hippocampal neurons. Beta-amyloid associates with HADH2. Soluble APP binds, via its N-terminal head, to FBLN1. Interacts with CPEB1 (By similarity). Interacts with ANKS1B.,tissue specificity:Expressed in all fetal tissues examined with highest levels in brain, kidney, heart and spleen. Weak expression in liver. In adult brain, highest expression found in the frontal lobe of the cortex and in the anterior perisylvian cortex-opercular gyri. Moderate expression in the cerebellar cortex, the posterior perisylvian cortex-opercular gyri and the temporal associated cortex. Weak expression found in the striate, extra-striate and motor cortices. Expressed in cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma. Isoform APP695 is the predominant form in neuronal tissue, isoform APP751 and isoform APP770 are widely expressed in non-neuronal cells. Isoform APP751 is the most abundant form in T-lymphocytes. Appican is expressed in astrocytes.,
展开内容
功能:
G2 phase of mitotic cell cycle, mitotic cell cycle, cell morphogenesis, cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation,suckling behavior, regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, mRNA polyadenylation, RNA processing, mRNA processing, regulation of translation, protein amino acid phosphorylation, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphate metabolic process, cellular ion homeostasis, cellular calcium ion homeostasis, cellular metal ion homeostasis, cellular copper ion homeostasis, endocytosis, apoptosis,induction of apoptosis, cell motion, microtubule-based process, microtubule-based movement, cell cycle, cell adhesion,cell surface receptor linked signal transduction, regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor activity, glutamate signaling pathway, Notch signaling pathway, cell-cell signaling, synaptic transmission, regulation of mitotic cell cycle,axonogenesis, axon guidance, synaptogenesis, muscle organ development, skeletal muscle tissue development,neuromuscular junction development, behavior, learning or memory, learning, mating behavior, mating, locomotory behavior, feeding behavior, visual behavior, cell recognition, neuron recognition, axon cargo transport, cell death,adult locomotory behavior, regulation of cell size, visual learning, response to radiation, response to light stimulus,response to abiotic stimulus, positive regulation of biosynthetic process, membrane invagination, regulation of receptor activity, positive regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process, positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process, posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression, positive regulation of gene expression,regulation of cell death, positive regulation of cell death, microtubule-based transport, programmed cell death,induction of programmed cell death, striated muscle tissue development, membrane organization, cell growth, mRNA metabolic process, vesicle-mediated transport, axon choice point recognition, axon midline choice point recognition,death, phosphorylation, neuron remodeling, dendrite development, reproductive behavior, regulation of phosphate metabolic process, transmission of nerve impulse, cellular homeostasis, developmental maturation, cell cycle process,cell cycle phase, biological adhesion, cellular cation homeostasis, cellular di-, tri-valent inorganic cation homeostasis,cell projection organization, neuron differentiation, extracellular matrix organization, adult behavior, cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport, forebrain development, RNA 3'-end processing, mRNA 3'-end processing, neuron projection development, positive regulation of cellular biosynthetic process, regulation of cellular protein metabolic process, endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis, regulation of cellular component size, cellular component morphogenesis, cell part morphogenesis, ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway, growth, regulation of growth, regulation of multicellular organism growth, regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway,regulation of phosphorylation, neuron maturation, homeostatic process, muscle cell differentiation, regulation of apoptosis, extracellular structure organization, positive regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death,positive regulation of programmed cell death, regulation of kinase activity, RNA polyadenylation, regulation of transcription, positive regulation of cell cycle, regulation of protein kinase activity, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle, positive regulation of nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolic process, positive regulation of transcription, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, intracellular transport, cell maturation, developmental cell growth, developmental growth,neuron development, cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation, collateral sprouting, collateral sprouting in the absence of injury, skeletal muscle fiber development, muscle fiber development, neuron projection morphogenesis, cell projection morphogenesis, chemical homeostasis, ion homeostasis, regulation of synapse structure and activity, synapse organization, neurological system process, neuromuscular process controlling balance,cognition, neuromuscular process, synaptic growth at neuromuscular junction, striated muscle cell differentiation,positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process, regulation of phosphorus metabolic process, regulation of RNA metabolic process, positive regulation of RNA metabolic process, G2 phase, interphase, interphase of mitotic cell cycle, regulation of transferase activity, neuron apoptosis, smooth endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis,behavioral interaction between organisms, regulation of cell cycle, muscle cell development, striated muscle cell development, metal ion homeostasis, di-, tri-valent inorganic cation homeostasis, copper ion homeostasis, calcium ion homeostasis, cation homeostasis, cellular chemical homeostasis, muscle tissue development, skeletal muscle organ development,
展开内容
细胞定位:
Cell membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Perikaryon . Cell projection, growth cone . Membrane, clathrin-coated pit . Early endosome . Cytoplasmic vesicle . Cell surface protein that rapidly becomes internalized via clathrin-coated pits. Only a minor proportion is present at the cell membrane; most of the protein is present in intracellular vesicles (PubMed:20580937). During maturation, the immature APP (N-glycosylated in the endoplasmic reticulum) moves to the Golgi complex where complete maturation occurs (O-glycosylated and sulfated). After alpha-secretase cleavage, soluble APP is released into the extracellular space and the C-terminal is internalized to endosomes and lysosomes. Some APP accumulates in secretory transport vesicles leaving the late Golgi compartment and returns to the cell surface. APP sorts to the basolateral surface in epithelial cells. During neuronal differentiation, the Thr-743 phosphorylated form is located mainly in growth cones, moderately in neurites and sparingly in the cell body (PubMed:10341243). Casein kinase phosphorylation can occur either at the cell surface or within a post-Golgi compartment. Associates with GPC1 in perinuclear compartments. Colocalizes with SORL1 in a vesicular pattern in cytoplasm and perinuclear regions. .; [C83]: Endoplasmic reticulum . Golgi apparatus . Early endosome .; [C99]: Early endosome .; [Soluble APP-beta]: Secreted .; [Amyloid-beta protein 42]: Cell surface. Associates with FPR2 at the cell surface and the complex is then rapidly internalized. .; [Gamma-secretase C-terminal fragment 59]: Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Located to both the cytoplasm and nuclei of neurons. It can be translocated to the nucleus through association with APBB1 (Fe65) (PubMed:11544248). In dopaminergic neurons, the phosphorylated Thr-743 form is localized to the nucleus (By similarity). .
展开内容
信号通路
文献引用({{totalcount}})
Recently Viewed Products
Clear allToggle night Mode
{{pinfoXq.title || ''}}
Catalog: {{pinfoXq.catalog || ''}}
Filter:
All
{{item.name}}
{{pinfo.title}}
-{{pinfo.catalog}}
主要信息
Target
{{pinfo.target}}
Reactivity
{{pinfo.react}}
Applications
{{pinfo.applicat}}
Conjugate/Modification
{{pinfo.coupling}}/{{pinfo.modific}}
MW (kDa)
{{pinfo.mwcalc}}
Host Species
{{pinfo.hostspec}}
Isotype
{{pinfo.isotype}}
产品 {{index}}/{{pcount}}
上一个产品
下一个产品
{{pvTitle}}
滚轮缩放图片
{{pvDescr}}